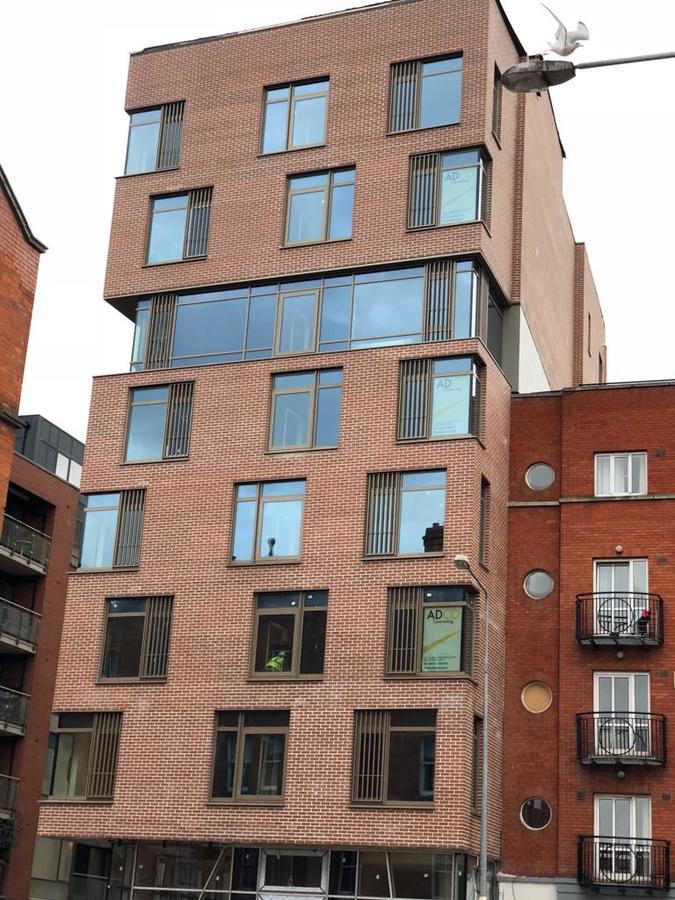
The purpose of low emission coating is the reduction of heat loss through the windows by the reflection of infra-red radiation back into the room. The first low emission coatings were applied onto the soft glass surface during the cooling phase of the float production process, and are called "hard" or "on-line" coatings. They were more durable, but also more noticeable and not as effective as modern coatings, which are applied in the "off-line" process and called "soft". Compared to "hard" coatings they are almost invisible and are very effective in the prevention of heat losses through the large glazed areas of modern buildings. The most popular are Low-E 1.1 and Low-E 1.0 coatings, which provide U value respectively 1.1 and 1.0 W/m²K in double insulating glass units, and 0.5 W/m²K in triple insulating glass units. There are also special Low-E coatings for passive house glazing, with improved solar energy transmission, intended for use in triple insulating glass units only.
AluFactory Ltd
Contacts
Commercial
Aleks Pogarcevs
aleks@alufactory.com
info@alufactory.com
Mobile:
Mobile Telephone Number:
+353 (86) 174 7468
Office:
Office Telephone number:
+353 (1) 842 2899
Commercial
Joe Garry
joe.g@alufactory.com
info@alufactory.com
Mobile:
Mobile Telephone Number:
+353 (0) 86-8585272
Office:
Office Telephone number:
+353 (1) 842 2899
Residential
Sales department
sales@alufactory.com
Mobile:
Mobile Telephone Number:
+353 (86) 011 3829
Office:
Office Telephone number:
+353 (1) 842 2899

SIA AluFactory ir noslēdzis 2021. gada 22. februārī līgumu Nr. SKV-L-2021/32 ar Latvijas Investīciju un attīstības aģentūru par atbalsta saņemšanu pasākumam "Starptautiskās konkurētspējas veicināšana" ietvaros, ko līdzfinansē Eiropas Reģionālās attīstības fonds.
© Alufactory
2020-2025
Made by Taurus